
Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis systems are a purification technology that separates ions in water by forcing water through membrane pores under high pressure. Especially industrial reverse osmosis systems are one of the indispensable pieces of equipment in the industry.
Reverse osmosis, or as it is commonly known in the world and industry, is a membrane-based water purification technique used to separate ions from water. This technique is based on the principle of filtering water containing dissolved ions through specially selective membranes under high pressure. While the membranes allow water to pass through, they act as a barrier against other ions, preventing their passage and thus enabling the purification process. When examined in terms of cost/benefit in today's technology, we can easily say that the most suitable purification technique in the industry is industrial reverse osmosis.
Our Reverse Osmosis Systems
Check out the product groups designed for specific purposes
Small and Medium-Sized RO
Check our reverse osmosis systems with capacities ranging from 0.25 m3/h to 5 m3/h.

Large Scale RO
Check ou reverse osmosis systems with capacities ranging from 5 m3/h to 200 m3/h.

Seawater Desalination RO
Check our seawater purification and desalination systems between 0.25 m3 and 100 m3/h.


Applications of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Industrial reverse osmosis systems are used for various purposes in many different fields, especially in industrial water treatment processes. The most preferred areas and processes for these systems are:
- Supply of drinking water from seawater or other sources that are not suitable for drinking
- Treatment of boiler feed water in boilers
- Production of ultra-pure water in the microelectronics sector
- Production of high-purity water for the pharmaceutical industry
- Process water treatment in beverage production
- Production processes of dairy products and many other food products in the food sector
- Recovery of industrial waste or applications for rehabilitating and releasing it into nature
Industrial-type reverse osmosis systems with different design features are used in all other areas of industry.
About Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water treatment technology that can remove contaminants such as dissolved salts, microorganisms and organic matter from water at a high rate using a semi-permeable membrane. This method, which works by reversing the natural osmosis process, has become one of the cornerstones of industrial water treatment today. It plays an important role in the recovery of salty or unusable water as drinking water or process water. For example, reverse osmosis is most commonly used to desalinate seawater to obtain drinking water. As of 2019, approximately 16,000 desalination plants worldwide were producing a total of ~95 million m³/day of water with reverse osmosis technology (approximately half of this capacity is in the Middle East and North Africa region). Reverse osmosis plays a critical role by providing fresh water in regions where water resources are limited and by providing high purity water in industrial processes.
Reverse osmosis is positioned as one of the most sensitive and advanced treatment steps in general water treatment processes. Conventional methods such as filtration, sedimentation or disinfection are effective in removing suspended solids and microbes, but cannot remove dissolved ions and salinity. Reverse osmosis, on the other hand, provides demineralization by separating water molecules from other ions and molecules with the principle of membrane separation. Therefore, reverse osmosis is generally used to provide the final purity of water after pre-treatment steps such as sand filtration, ultrafiltration and activated carbon . RO is considered as the “polisher” or final stage technology in the water treatment process chain because it performs the finest purification . The product water obtained is usually of a quality that will meet drinking water standards or relevant industrial purity standards. As a result, reverse osmosis has an indispensable position in both drinking water supply and industrial water preparation by providing pure water production at a level that cannot be reached with traditional methods.
Working Principle of Reverse Osmosis
Difference Between Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis
Osmosis is a natural process that occurs when two environments with different solution concentrations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane. Water tends to balance the concentrations by passing through the membrane from the side with lower concentration (less salty) to the side with higher concentration. This transition occurs thanks to the osmotic pressure depending on the solution concentration difference. In reverse osmosis, this natural flow direction is reversed by applying pressure from the outside. In other words, with the help of high pressure, water is forced from the side with high salt concentration (e.g. sea water) to the side with low salt concentration (pure water). In this way, the membrane passes water molecules while holding back larger ions and molecules. In order for the reverse osmosis process to occur, the applied pressure must exceed the osmotic pressure of the feed water. For example, in sea water desalination, high pressures such as ~60–80 bar are used to overcome the osmotic pressure (approximately 30 bar); thus, water molecules are separated from salt water and passed to the clean water side.
Structure and Operation of Reverse Osmosis Membranes
Modern reverse osmosis membranes are generally manufactured from a thin film composite (TFC) structure, polyamide-based material. The active separation layer is a very thin film, approximately 2000 Å (0.2 µm) thick, which allows water to pass through while largely rejecting dissolved salts. This active layer is placed on a highly porous substrate to provide mechanical support. Reverse osmosis membrane elements are usually in the form of spiral-wound modules in industrial applications. In a spiral-wound membrane element, a mesh-shaped spacer is placed between the two membrane layers to create a flow distance, and the edges are glued to form an envelope structure. This envelope-like membrane package is wrapped around a central perforated collection tube with a porous support layer called the permeate carrier. The envelopes are sealed with adhesive on three edges, and the open edge is connected to the central collection tube. The feed water flows turbulently on the membrane surface thanks to this spacer and the water molecules pass through the membrane and move towards the central tube along the permeate carrier inside the envelopes. The ions that cannot pass through the membrane surface are carried away with the flow to the outside of the envelope and form the concentrate stream. Thus, a single feed stream is separated into two separate streams after leaving the membrane module: permeate (product water) and concentrate (retentate/reject).
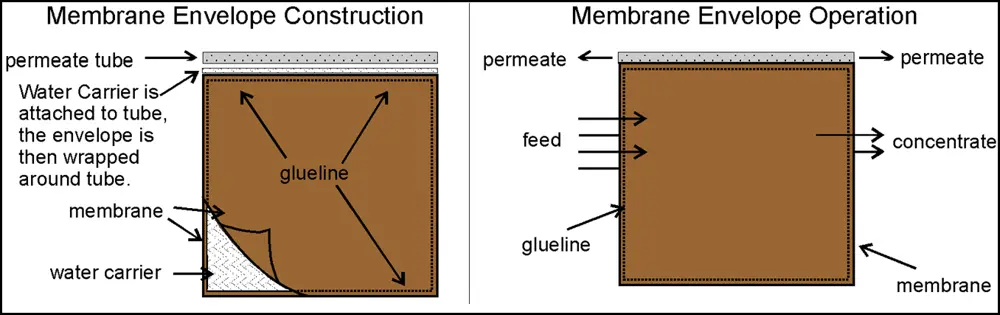
Figure 1: Cross-flow principle in reverse osmosis membrane. The membrane system divides a feed stream into two: purified water (permeate) passes through the membrane, while the remaining part is discharged as a concentrate stream, concentrating the contaminants. This cross- flow filtration minimizes the formation of deposits on the membrane surface; if there was a single outlet stream (such as dead-end filtration), the membrane would quickly become clogged. Spiral wound RO elements create a continuous washing effect with the principle that the water fed from the front flows parallel to the membrane surface and the concentrate flow exits from the sides. This structure ensures the efficient operation and long life of the membrane. Purified water passing through the membrane is collected in the permeate collection tube in the center of the element.
Pressure, Flow and Membrane Behavior
In reverse osmosis systems , operating pressure is the primary determinant of system performance. As applied pressure increases, the flux through the membrane increases ; however, each membrane has a maximum flux capacity and a risk of decreased salt retention efficiency in the event of overpressure. A well-designed RO system will typically retain 95–99% of the dissolved solids in the feedwater. For example, a feedwater with a TDS of 500 mg/L can yield product water with a TDS of <10–25 mg/L under appropriate conditions. As water flows through the membrane, some of the water is removed as permeate, while the rest is removed as concentrate. The recovery rate indicates how much of the feedwater is collected as permeate and is usually in the range of 50–80% (depending on the quality of the feedwater). High recovery means less wastewater, but increases the salt concentration in the concentrate, increasing the risk of scale formation on the membrane. Therefore, an optimum recovery is selected for each application. In addition, temperature is a parameter that affects water flow: At higher temperatures, the viscosity of the water decreases, which increases the membrane flux, but the osmotic pressure also increases, which may increase salt permeability to some extent. Therefore, RO systems are usually designed for a reference temperature of 20–25°C, and performance evaluations are carried out by temperature normalization. As a result, the operating principle of reverse osmosis is to separate water under high pressure with a semi-permeable membrane, to keep the membrane surface clean with cross-flow operation, and to optimize the operating parameters according to water quality.
Main Components of Reverse Osmosis Systems
An industrial reverse osmosis system consists of several subunits that complement each other to transform water from raw to pure water suitable for use. The main components are:
Pretreatment Systems
Depending on the nature of the feedwater, pretreatment is essential to protect RO membranes and ensure their efficient operation. Pretreatment typically involves one or more steps. Sand or multi-media filtration prevents particulate clogging of membranes by retaining suspended solids that cause turbidity in the water. Microfiltration or ultrafiltration units can be used to remove finer particles and turbidity, especially in high-load feedwaters such as surface water or wastewater. Activated carbon filters remove free chlorine and organic matter from the feedwater – critical to remove beforehand, as chlorine can chemically degrade (oxidize and “burn”) thin-film RO membranes. Activated carbon also removes taste and odor-causing substances, improving the organoleptic quality of the water. Again, pretreatment may include softening (ion exchange) or dosing of antiscalants, depending on the hardness of the water . In this way, the saturation levels of hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium or species that can form scale such as sulfate and silica are reduced and the formation of limestone (scale) on the membrane is prevented. Finally, if there are microorganisms in the feed water that have the potential to grow biologically, the biological load can be reduced by using UV disinfection devices or biocidal agents at the inlet. A well-designed pretreatment extends the life of RO membranes and reduces operating costs by reducing the frequency of cleaning.
High Pressure Pump
Pre-treated water is fed under high pressure to pass through the RO membranes. The high pressure pump, which is considered the heart of the system, performs this job. The pump is typically a stainless steel centrifugal pump, depending on the design requirement, and can provide operating pressures from 10 to 80 bar (depending on the feed water salinity). There may be a pressure regulation valve or a bypass line to control and maintain the pressure at the pump outlet. In large-scale RO plants, variable frequency drives (VFDs) are used in pumps for energy efficiency; this allows the pump speed to be adjusted to reach the desired pressure and protects the membranes from sudden pressure increases. In addition, safety (pressure relief) valves are installed to prevent excessive pressure build-up in the high pressure line.
Membrane Modules
The main component where the reverse osmosis process takes place is the membrane module. Spiral-wound membrane elements are typically standard 4-inch or 8-inch diameter cylindrical modules and are placed in series in pressure vessels (housing). Each module is constructed by tightly wrapping semipermeable membrane sheets and spacers (Figure 2). Feedwater enters each pressure vessel inlet and gradually concentrates as it passes through the series-connected membrane elements and exits at the end. During this time, a certain amount of permeate from each element is collected in the tubes at the center of the membranes. Membrane modules can be arranged as single-stage or multi-stage systems, depending on the arrangement of the system. Pressure gauges are provided at each module outlet or pressure vessel head and flow meters are provided on each stream to monitor the performance of the membranes. Membrane modules are replaced at regular intervals (e.g. 3–5 years) as performance deteriorates; this period can be extended with good pretreatment and operation.
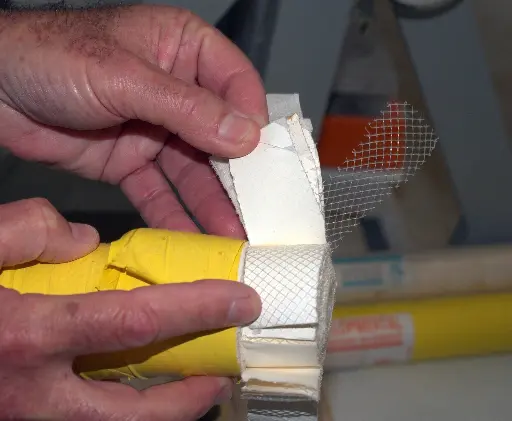

Figure 2: Layers of a spiral wound RO membrane element. The structure of a membrane element is shown in the photo by opening the outer winding. The yellow pipe in hand is the central permeate collection tube of the element . The white layers wrapped around the tube are semi-permeable membrane leaves , and the mesh-like material between them is the feed spacer network . In addition, there is a permeate carrier layer on the back surface of the membrane leaves, which allows the permeate to be transported to the center. Thanks to this layered structure, the feed water flows by dispersing along the membrane leaves, while pure water passes through the membranes and moves along the carrier to the center, salts and other impurities cannot pass the membrane and are concentrated in the waste stream.
Flow Control Equipment
Various instrumentation and control elements are used for stable and safe operation of RO systems. Pressure gauges monitor system pressures at the pump outlet and at the inlet/outlet of each membrane pressure vessel. Flow meters measure flow rates in the feed, permeate and concentrate lines to monitor the water balance of the system. In this way, the recovery rate can be calculated instantly and it is ensured that design values are not exceeded. Conductivity (TDS) sensors monitor product water quality; feed and permeate conductivities are measured to calculate salt recovery for membrane performance monitoring (a good membrane typically provides over 95% salt rejection). Automatic control valves are located especially in the concentrate outlet line and are used to adjust system pressure/recovery. These valves, with electric or pneumatic actuators, open and close according to signals from the control system, creating a constant flow and pressure regime. In larger RO units, a PLC or control panel constantly monitors the data from these sensors and provides automation by adjusting pump speed and valve positions. Additional instruments such as temperature meters, pH meters and, if necessary, ORP sensors can be used to monitor water properties and detect possible anomalies. Finally, back pressure prevention check valves and leak/dry run sensors are also part of the flow control system for safe operation.
Final Treatment Processes
Since the water obtained from the reverse osmosis membrane is very low in minerals and has a high saturation rate, final adjustments may be required in some applications. pH adjustment is done to balance the pH that has fallen in the RO product water, especially due to natural organic acids and carbon dioxide. For example, before using it as drinking water, RO water is slightly alkalized to prevent it from corrosiveness in the pipes (calcite filters or sodium hydroxide dosing can be used for corrosion control). Mineral balancing (remineralization) is also common for drinking water; completely demineralized water can have a bland taste and some minerals are desired to be regained for human consumption. For this purpose, methods such as passing through calcium carbonate beds or dosing mineral salts are applied. Disinfection , although the water leaving the RO process is almost completely free of bacteria and viruses, is important to prevent re-contamination when it is given to the distribution system. Especially in municipal drinking water production, a permanent disinfectant such as chlorine or chloramine is added to the RO product water. Alternatively, if it is to be stored, water tanks can be protected with UV disinfection devices. In some industrial applications, RO product water may be subjected to further purification steps (e.g. electrodeionization, ultraviolet organic removal, 0.2 micron absolute filtration). Such polishing processes are necessary to obtain ultrapure water, especially in the electronics and pharmaceutical industries. As a result, the main components of reverse osmosis systems are designed as a whole to produce water of targeted purity from raw water, and each component plays a critical role in system performance.

Figure 3: An industrial reverse osmosis water treatment unit. Pre-filters such as sand/activated carbon in stainless steel tanks on the right, RO membranes in horizontal cylindrical pressure vessels on the left, pump and control panel in the foreground. This type of system is designed to obtain high purity product water by passing raw water through several stages in applications such as bottled drinking water production.
Stages in the Reverse Osmosis Process
Water purification in a reverse osmosis system occurs in several basic, sequential stages:
Pre-treatment Process
Raw water must be brought to suitable conditions before entering the reverse osmosis membranes. Pre-treatment, as detailed in section 3, protects the membranes by removing suspended solids, chlorine, hardness ions and microorganisms from the water. This stage is critical for the healthy operation of the RO process. In systems with inadequate pre-treatment, membranes quickly become dirty, pressure losses increase and efficiency decreases. For example, turbid well water is first clarified by passing through a sand filter and a cartridge filter, then passed through an active carbon filter to remove chlorine and fed to the RO unit by adding an antiscalant dose. In this way, the water reaching the membrane inlet carries as little sediment, biological and scalen load as possible.
Membrane Filtration (RO stage)
Pre-treated water is fed to the reverse osmosis membrane(s) by a high-pressure pump. With the membrane filtration that takes place inside the RO modules, water molecules pass through the membrane structure and are collected as permeate, while dissolved salts and other contaminants are condensed in the concentrated stream and discharged. In industrial systems, multi-stage systems are generally used to achieve the desired recovery and water quality. For example, in a multi-stage system, the concentrated water coming out of the first stage becomes the feed of the next stage. In this way, the total recovery rate can be increased (for example, 50% permeate is taken in the first stage and the concentrate is fed to the second stage, achieving a total recovery of 75–80%). On the contrary, in multi-pass systems, the permeate water is passed through another RO membrane again and made even purer (double-pass RO is used especially in sectors such as semiconductor and pharmaceuticals where ultrapure water is required). Another issue that needs to be considered in the membrane filtration stage is the management of concentrated/reject water. The concentrated stream resulting from RO must be discharged appropriately due to its high salt and pollutant content. In a seawater treatment plant, the concentrate can be discharged directly into the sea (the mixing ratio is adjusted by performing environmental impact assessments), but in inland brackish water treatment plants, the concentrated water is usually directed to wastewater lines, deep well injections or evaporation ponds. This concentrated stream is an unavoidable by-product of the RO process and must be managed as part of the overall treatment efficiency.
Final Treatment Processes
Permeate water obtained from membranes is subjected to some final treatments depending on the purpose of use. If drinking water is obtained, the pH of the permeate water is generally corrected to the slightly alkaline side and calcium-magnesium ions can be added to the water to make it harder (for example, by passing it through marble filters). This process provides the water with a more balanced and drinkable character. Chlorination is then performed in the distribution network to ensure biological safety. On the other hand, in industrial uses such as boiler feed water, RO permeate is sent to deionization units (ion exchange or electrodeionization) to remove the last remaining trace ions and thus water with very low conductivity is obtained. The obtained product water is stored or directly delivered to the point of use after it complies with the relevant standards. If the water exiting the RO system is to be stored, periodic UV irradiation or protective chlorination can be applied to prevent bacterial growth in the tank. The final treatment stage includes the final touches necessary to make the water suitable for final use. In this way, RO permeate reaches a quality that can be used safely, whether it is drinking water or industrial process water.
Parameters to be Measured and Controlled
For a reverse osmosis plant to operate efficiently and safely, various parameters related to both inlet water and process and outlet water need to be measured and monitored regularly:
Influent Water Quality
The characteristics of the feed water have a direct impact on the design and performance of the RO system. Therefore, the basic quality parameters of the water entering the RO unit should be monitored. Total dissolved solids (TDS) or electrical conductivity indicate the salinity level of the raw water and determine the osmotic pressure. For example, a sudden increase in the raw water TDS value may indicate a change in the feed water source (salt contamination or contamination). The pH value indicates the acidic or basic character of the water; although RO membranes can generally operate in the pH range of 3–11, extreme pH values can damage the membrane material or increase the susceptibility to scale formation. The hardness (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺ concentrations) and alkalinity parameters are critical for determining the potential for scale formation, especially calcium carbonate. Turbidity and suspended solids indicate how well the water requires pretreatment; if turbidity is high, more effective filtration measures should be taken. Since the presence of chlorine (Cl₂) or chloramine can damage RO membranes (through oxidative effects), residual chlorine should be measured at the active carbon filter outlet or RO inlet to ensure that it is close to zero. Metals such as iron and manganese are also monitored and are generally kept at <0.1 mg/L, as they can accumulate on membranes even at low concentrations and cause problems. Bacteriological load (e.g. heterotrophic plateau count) is also monitored in the feed water; if a high microbial load is detected, disinfection/UV steps are increased in the pretreatment. The measurement of these inlet water parameters is important to check whether the water is in suitable conditions before entering the RO system and whether the pretreatment is working properly.
Operating Parameters
Key operating parameters that determine the performance of the RO system during operation should be monitored continuously or periodically. The pressure values are the most important of these; the high pressure pump outlet pressure and the concentrate pressure at the end of each stage/vessel are monitored. The transmembrane pressure difference across the membranes is an important indicator as it can be an indication of fouling. Flow rates are measured separately for feed, permeate and concentrate streams. This allows the instantaneous recovery rate to be calculated: for example, if 100 L/min feed and 75 L/min permeate, the recovery is 75%. Changes in flow rates (for example, a decrease in permeate flux over time) may indicate membrane fouling or increased pressure loss. Temperature is monitored as it affects membrane performance and the performance data is normalized to a standard temperature (25°C). The pressure difference (delta-P) across the feed and concentrate stream is another critical indicator; increasing pressure drop across the elements is an indication of fouling accumulation. One of the indirect indicators of membrane fouling is the increase in salt permeability: If the normally low product water conductivity starts to increase, salt retention may be decreasing due to contaminants accumulating on the membrane surface or membrane damage. Therefore, permeate conductivity or salinity is checked regularly. In addition, operating parameters such as pump flow rate, energy consumption , and the amount of dosed chemicals are monitored to ensure efficient operation of the system. By following the trends in these parameters, operators can diagnose the source of the problem when an abnormal situation occurs (for example, a decreasing permeate flux despite increasing pressure). For example, if the permeate flow rate is lower than expected at a certain pressure, it can be concluded that the membranes are fouled and cleaning is planned.
Product Water Quality and Standards
The quality of the permeate water, which is the final output of the reverse osmosis system, should be continuously monitored to ensure that it is suitable for the intended use. Conductivity or TDS is the most basic indicator of product water quality; usually the RO effluent conductivity is less than 1% compared to the raw water. If drinking water is being produced, the TDS value should be ~<500 mg/L (according to standards), which is easily achieved in most cases with RO (even with some mineral back-dosing if necessary, see post-treatment). pH is kept within a certain range, especially for human consumption or industrial process requirements (for example, usually 6.5–8.5 for drinking water). Since RO water can often be slightly acidic, this value is monitored after pH adjustment. Hardness is checked for drinking water or boiler water; although RO permeate is usually very low, <1°F, adjustments are made if the downstream process requires it. Silica concentration is a parameter controlled in applications requiring high purity or in steam boilers; RO alone removes most of the silica, but if very low levels are required, a second RO pass or ion exchange may be required. Total organic carbon (TOC) is particularly important for the electronics and pharmaceutical industries; although RO retains most of the organics, additional steps are taken for TOC at ppb levels. In addition, microbiological analyses (coliform, E. coli, etc.) are performed for drinking water if necessary – although RO membranes largely remove bacteria and viruses, samples are taken from the outlet to prevent contamination after the system. Product water quality must comply with national and international standards; World Health Organization (WHO) and local regulatory limit values for drinking water, and relevant process standards for industrial water (e.g. boiler water standards, ASTM electronic water standards). Regular measurement of these parameters indicates whether the system is achieving its intended purification performance and allows intervention in case of any deviations.
Interpretation of Parameters and Fault Diagnosis
Not only recording the measured data but also interpreting it is essential for a successful operation. For example, it is calculated with the formula salt rejection rate = [(feed conductivity – permeate conductivity) / feed conductivity] × 100 and should be constantly high (such as >95%). If salt rejection starts to decrease, the possibility of leakage or chemical damage in the membranes is evaluated. If the pressure difference increase is determined, it is understood whether there is fouling in the membranes in that stage by looking at which stage the increase occurs (an increase in the first stage is generally a sign of fouling, and an increase in the last stage is generally a sign of scaling). If the permeate flux decreases over time, it is normalized by taking into account temperature changes and pressure changes; if there is a real decrease, the membrane surface may be clogging. In this case, chemical cleaning is planned. If the recovery rate has fallen below the target, it is thought that there may be a problem in the concentrate control valve or in the feed. If the desired flow cannot be achieved despite the pump pressure increasing, there may be clogging in the filters or a loss of pump performance. In all these scenarios, the fault diagnosis is made by evaluating the monitored parameters together and the problem is solved. For example, if an increase in permeate conductivity + an increase in permeate flux is observed, this usually indicates a fault such as membrane rupture or O-ring leaks (because both water passes easily and salt retention decreases). In light of this data, operators quickly intervene and perform membrane replacement or repair. As a result, each parameter measured in reverse osmosis systems normally moves within a certain range and the health of the system is preserved by carefully interpreting the trends in these values.
Industrial Usage Areas
Reverse osmosis systems are widely used in many sectors that require high purity water or want to recycle salty/waste water. The main industrial areas of use and their applications in these areas can be summarized as follows:
Food and Beverage Industry
Sub-sectors such as bottled drinking water, soft drink production, beer and dairy products attach great importance to the quality of the water used in their products. RO is generally used in this sector to completely purify raw water and rearrange the desired mineral profile. For example, large beverage companies remove all minerals and taste-affecting substances with reverse osmosis to bring water sources in different geographical regions to a standard taste and composition, then add back certain minerals in a controlled manner. In this way, product flavor and quality are maintained. In addition, RO is preferred in soft drink and fruit juice production facilities because it also increases microbiological safety. In the dairy industry, reverse osmosis is used in processes such as whey concentration; it is possible to obtain protein-rich concentrate by partially removing water and lactose from whey, a by-product of milk, with RO. RO systems used in food businesses are generally designed from stainless material and suitable for sanitation. As a result, reverse osmosis is a key technology for the supply of pure water that ensures product quality in the food and beverage sector.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
Processes such as semiconductor chip manufacturing, LCD panels, solar panels, and precision electronic component manufacturing require the use of ultra pure water. The water used in this industry has one of the highest purity standards in the world: resistivity 18.2 MΩ cm, total organic carbon < 1 ppb, and particulate matter counts that are almost non-existent. To achieve this level of water, multistage purification processes are usually used, with reverse osmosis being one of the first important steps in this process. In a typical electronic-grade water system, municipal water is first largely desalinated and organic by RO, followed by additional steps such as deionization units, ultrafiltration, UV oxidation, and microfiltration to bring the water close to "9N" purity (i.e. 99.9999999% pure). RO takes most of the load here, extending the life of subsequent units. In semiconductor factories, huge capacity RO facilities both prepare water used as washing rinse water in production and play a role in recycling by repurifying process wastewater. Since continuity and consistency are critical in water systems in the electronics sector, reverse osmosis units are usually arranged as double-pass and redundant. In this way, ultra pure water , known as the purest water in the world, is obtained with a series of advanced purification technologies including reverse osmosis and supplied to production lines.
Energy Industry (thermal power plants and boiler feed water)
Thermal power plants and steam boilers of industrial plants require high purity water as feed water. Since water evaporates and condenses in boilers, even the slightest impurities in the water can accumulate over time and lead to deposits such as limestone, silica or corrosion products in pipes and turbines. For this reason, the feed water of high-pressure steam boilers is usually demineralized water , which is deionized water. Reverse osmosis is widely used as an economical step in this demineralization process. For example, in a power plant, raw water (which can be river or well water) is first passed through an RO system to remove 98-99% of the dissolved substances. The remaining trace ions are then removed by mixed-bed ion exchangers or electrodeionization (EDI) to obtain pure water. The conductivity of this pure water is usually set at values such as <0.1 µS/cm and silica <20 ppb. The advantage of RO here is that it greatly reduces the load on ion exchange resins, reducing the need for chemical regeneration. In addition, RO-treated water is used in processes such as cooling towers to keep hardness and conductivity under control in the circulating water, thus preventing corrosion and scaling. Since the continuity and quality of water in the energy sector directly affects the efficiency of the operation, RO systems are among the critical infrastructure elements.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Water is an important input for sensitive chemical reactions and drug production. The pharmaceutical industry in particular must comply with very strict standards set by Pharmacopoeias for water used in production. Categories such as “Purified Water” and “Water for Injection (WFI)” used in drug production must be extremely pure in terms of microbiology and ionics. RO systems are often used as the first step in preparing such high purity water. For example, in a pharmaceutical factory, city water or purified water source is combined with reverse osmosis and then a second RO or steam distillation system with ultra-low permeability to obtain water close to water for injection. In the pharmaceutical industry, reverse osmosis is usually equipped with double-pass and hot water/chemical sanitation; thus, the system is regularly disinfected and the risk of bacterial contamination is managed. In the chemical industry, RO protects product purity by ensuring that the water to be used in reactions does not contain chlorine, hardness or heavy metals. For example, in areas such as paint, coating, battery production, petrochemicals, RO is used to obtain deionized water and use it in formulations. RO can also be used to recover wastewater from chemical plants; catalyst wash water or process waste can be purified with RO and brought to discharge standards or reused in the process.
Seawater Desalination
In many coastal cities and islands around the world, drinking and utility water needs are met by seawater desalination. The vast majority of these desalination applications are based on reverse osmosis membrane technology. When seawater (~35,000 mg/L TDS) is passed through RO membranes, the water molecules are separated from the salts to obtain water of drinking water standard (<500 mg/L TDS). This process typically requires high pressures of 60-70 bar, and energy costs are the largest expense. However, in recent years, the energy consumption of seawater RO plants has been significantly reduced by the use of energy recovery devices (such as pressure exchangers). For example, in modern SWRO (Sea Water RO) plants installed in countries such as Spain, Israel, and Saudi Arabia, the unit energy consumption of produced water has decreased to ~3 kWh/m³. In seawater desalination, the water after RO is usually partially remineralized and chlorinated to make it suitable for drinking water. In addition, seawater contains boron as a special challenge ; boron may not be maintained at the desired level in single-pass RO (WHO drinking water recommendation <0.5 mg/L). For this reason, a second RO pass (operated at high pH) is sometimes applied to remove boron in seawater plants. Apart from this, seawater RO systems are also designed to be durable in terms of materials (high alloy stainless steels, composite pipes) because the salty environment is corrosive. Seawater desalination plants have been established in regions such as Izmir and Antalya in Turkey, meeting the water needs of hotels and settlements. In summary, reverse osmosis is a leader in desalination due to its much lower energy consumption compared to vacuum distillation methods and its developing membrane technology.
Municipal and Industrial Wastewater Recovery
Increasing water scarcity and environmental requirements have brought the reuse of wastewater by treating it to the agenda. Reverse osmosis is an important tool in bringing treated wastewater to reuse quality with advanced treatment. Especially in industrial wastewater treatment, RO is applied after biological treatment and filtration, and the water is brought to a purity that can be reused in the processes. For example, in the textile sector, wastewater containing dyes is treated with membrane bioreactor + RO and made usable again in the factory. Again, facilities that need a lot of water, such as refineries and petrochemical plants, try to close their water cycles by recovering their wastewater with RO. In municipal wastewater treatment plants, treated water can be polished with RO before being used as irrigation or industrial water. In some regions, such as Orange County (USA), RO is used to produce drinking water (near potential) from treated wastewater; In this application, wastewater is first fully treated with microfiltration, then RO and finally UV/AOP (advanced oxidation) and fed to groundwater to obtain indirect drinking water. In this way, the water cycle is closed and water resources are used sustainably. RO is preferred in wastewater recovery because it removes dissolved pollutants (e.g. nitrate, phosphate, heavy metals, organic micropollutants) with high efficiency. However, since the wastewater matrix is complex, FOULING control and cleaning frequency are important operating issues in these systems (See section 8). As a result, as wastewater recycling becomes more attractive from both environmental and economic perspectives, reverse osmosis will continue to play a key role in this area.
Parameters to be Purified by Reverse Osmosis According to Industries
Each industry requires a specific quality of water to be used in its processes. Reverse osmosis systems can be flexibly designed to meet the water quality goals of different industries. Below is a breakdown of the water quality criteria required in various industries and how these criteria affect RO design:
Food/Beverage Sector Water Quality
In beverage production, water is expected to be perfect in terms of taste, odor and microbiology . Therefore, RO purified water usually contains very low minerals such as <50 mg/L TDS; thus, the components that give water its own flavor are minimized. However, since completely pure water is not desired, minerals are added according to the product formulation or can be mixed with raw water up to the targeted conductivity. For example, a beverage factory can make a controlled mixture to keep the water after RO in the conductivity range of 50–100 µS/cm. Microbiological parameters are also critical in this sector: The water must meet drinking water standards in terms of values such as coliform, E. coli, total plate count. Although the RO membrane largely retains bacteria, UV sterilization and chlorination steps are integrated after the system to prevent re-contamination. The hardness of the water can also be important in food production; for example, beer producers may find that a certain hardness of water is suitable for their recipes. In this case, hardness is added to the RO product water with a controlled dosage. In RO system design, the use of stainless and hygienic equipment in the food sector (for example, 316L steel membrane housings, connections without dead volume) helps to meet the parameters. In addition, food-approved chemicals are used in CIP (cleaning in place) cycles. As a result, the parameters targeted with RO in the food and beverage industry can be summarized as: low TDS, neutral pH, zero chlorine, low TOC and close to zero microbiological load.
Electronic/Semiconductor Water Quality
Water quality in this sector is subject to very strict standards. The most critical parameter is conductivity/resistivity , and it is desired that the water is practically free of all ions (a target of 18 MΩ cm resistivity). Again, TOC (Total Organic Carbon) should be at very low levels such as < 5–10 ppb, because organic impurities can leave dirt on sensitive electronic circuits. The number of particles is also limited to nanometers; >0.1 µm particles in water are not desired, so ultrafiltration filters are used after RO. Silica content is of particular importance in this sector, because silica can accumulate in film devices that are thinned by evaporation; targets such as <1 ppb are generally in question. Although reverse osmosis retains ~98% of silica in a single pass, it is common to reach the desired levels with two-stage RO + mixed bed resin in this sector. Certain ions such as sodium, potassium, chlorine, boron are also reduced to <ppb levels in line with target values. In the electronics industry, although the pH of water is kept around neutral, the most important thing is its conductivity; since pH measurement becomes difficult in almost pure H₂O. There are standards such as ASTM D5127 for the water of this industry. Such high quality requirements in RO design usually require double-pass RO and then a polishing layer (mixbed ion exchange + ultrafiltration + UV). While the first RO purifies the majority of the water, the second RO targets especially difficult contaminants such as boron and silica. In addition, bacterial control is carried out with methods such as ozonization and hot water sanitation even when electronic water systems are in operation. In short, RO design for the semiconductor and electronics industry is adjusted to the extreme purity values and is considered as part of a whole water treatment train, not a stand-alone RO.
Energy Sector/Boiler Feed Water Quality
Water quality for steam boilers is determined by the operating pressure. While low-pressure boilers have some tolerable hardness and TDS, high-pressure supercritical boilers require almost zero hardness, zero silica and very low conductivity . For example, for a 60 bar boiler feed water, conductivity < 10 µS/cm, total hardness < 0.1 ppm CaCO₃, silica < 20 ppb may be required, while for a 150 bar boiler much stricter values such as conductivity < 0.2 µS/cm, silica < 5 ppb are required. Reverse osmosis provides most of these parameters: it removes hardness and alkalinity almost to zero, and removes most conductive species. However, since CO₂ (carbon dioxide) gas that may remain in the RO permeate can form carbonic acid in the boiler and cause corrosion, degassing is usually applied by heating the decarbonator or feed water tank after RO. Since oxygen is also harmful to steel boilers, RO water is passed through deaeration towers or reacted with chemical sodium sulfite before being fed. Chloride and sulfate ions are also important parameters in this sector; they should be kept at < ppm levels as they accelerate corrosion. A good RO + mixed bed resin combination can reduce these ions to < 0.1 ppm. In addition, hardness is definitely desired at < 0.02 ppm (RO permeate provides this in practice). In RO system design, special membranes with low silica permeability or second pass application can be planned in boiler water applications. For example, while normal membranes retain 90-95% of boron and silica, special high silica rejection membranes are selected. Since water cuts are unacceptable in power plants, RO systems are installed with backups and by-pass lines are available. As a result, RO design for boiler feed water is made for very low hardness and TDS targets and completed with sequential purification steps; Ensuring water chemical balance (pH, degassing) also becomes an integral part.
Chemical/Pharmaceutical Sector Water Quality
The quality of water entering chemical production processes affects product purity and reaction efficiency. Especially in the pharmaceutical sector, water is subject to Pharmacopoeia standards: European Pharmacopoeia and USP define specific TOC and endotoxin limits for Pure Water under conductivity 1.3 µS/cm (@25°C). Reverse osmosis is typically installed as a double-pass system and incorporated into the pharmaceutical water system with intermediate storage; the first pass removes most of the organics and ions, the second pass cleans the remaining traces. If the water meets the desired conductivity and TOC values after the second pass, it is delivered to the point of use. 0.05 µm ultrafiltration is often added at the final stage for endotoxin (pathogenic bacterial particles) removal. Therefore, RO parameter targets for pharmaceutical water are: conductivity ≈ 1 µS/cm, TOC < 50 ppb, bacteria < 10 cfu/100mL, endotoxin < 0.25 EU/mL. In the chemical industry, the parameters are process specific; for example, if it is to be used in a boiler, the boiler water criteria above apply, if it is to be used as a reaction solvent, it may be desired to be free of chloride or certain metals. When designing RO systems, if specific ions are critical (for example, ultra-low sodium or chloride requirements), a suitable membrane selection or double-pass planning is made. If Na⁺ < 50 ppb is desired in a battery chemical plant, a mixed-bed ion exchanger is used in addition to the RO permeate. As a result, water quality requirements in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors are determined by the relevant standards and process sensitivities; the reverse osmosis system is configured to meet these targets. The flexible design possibilities of the RO (series-parallel arrays, different membrane types, multi-pass installation, etc.) allow it to adapt to changing needs.
Operating Dynamics of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Long-lasting and efficient operation of reverse osmosis systems is directly related to the understanding and control of various fouling and performance-reducing effects on membranes. In this section, membrane fouling mechanisms, prevention strategies, cleaning and maintenance requirements, and efficiency improvement methods are discussed.
Membrane Fouling Mechanisms
Due to the very small porous structures of RO membranes, some of the unwanted substances in the feed water may accumulate on the membrane surface or in the pores over time, causing fouling. Sources of fouling are generally examined under three headings:
Biofouling
Bacteria, algae or fungi present in the feed water can attach to the membrane surface and multiply, forming a biofilm layer. This biological layer blocks the membrane pores, significantly reducing water flow and increasing the pressure difference. Since RO membranes are particularly sensitive to disinfectants such as chlorine, a continuous biocide cannot be kept in the system; this creates a favorable environment for microorganisms. Biofouling is usually a major problem in hot climates, waters rich in organic matter or in cases of inadequate pre-disinfection. Symptoms include a rapid increase in pressure drop and foul odor/color in the first membrane pressure vessel.
Chemical Fouling (scaling and organic accumulation)
When it comes to chemical fouling, there are two main types: scaling and organic fouling . Scaling refers to inorganic salts that are dissolved in the feed water but exceed the solubility limit in the concentrated stream and precipitate as solid residue on the membrane. The most common type of scale is calcium carbonate (limestone); in addition, compounds such as calcium sulfate, barium sulfate, silica, calcium phosphate can also precipitate under certain conditions. Scalant accumulation forms a hard layer on the membrane surface, both reducing the flow and increasing salt permeation (because it narrows the effective pore area of the membrane). Organic fouling is the adhesion of natural organics such as colloids, humic/fulvic acids or industrial oils, polymers in the water to the membrane and forming a layer. Especially in surface waters and wastewaters, high molecular weight organics can leave a brown/sticky film layer on RO membranes. This also leads to a similar decrease in flux. Organic fouling is often seen in the first stages and in elements close to the feed inlet.
Physical Fouling (particle/colloidal fouling)
If the pretreatment is not fully effective, micron-sized particles or colloidal clay, silt, etc. can accumulate on the membrane surface. This accumulation occurs mostly at the inlet end of the membrane elements and manifests itself with a serious increase in pressure loss in a short time. In waters with a high silt density index (SDI), if a remedial pretreatment is not applied before RO, this type of physical fouling is inevitable. Physical fouling is relatively easy to reverse; it can be largely removed by chemical cleaning or rinsing, but if repeated frequently, it can roughen the membrane surface and pave the way for other types of fouling.
Fouling Prevention Strategies
Although it is not possible to completely prevent membrane fouling, various strategies are applied to minimize it. The most important strategy is appropriate pretreatment design and operation. Depending on the quality of the feed water, multi-stage filtration, softening, active carbon and, if necessary, ultrafiltration steps are planned to reduce the load on the membrane. In order to prevent biological fouling, methods are investigated to prevent biofilm formation on the membrane after the chlorine is removed from the feed water; for example, monthly/periodic chemical biocide cleaning or continuous low-dose biocide (e.g. isothiazolone) can be dosed to the feed water (however, these chemicals must be of a type and concentration that does not damage the membrane). Dosing of antiscalant chemicals is a standard practice in preventing scaling; these chemicals interact with ions such as calcium and barium in the feed water and disrupt the crystal structure, preventing precipitation. The appropriate antiscalant type and dose for each water is determined by saturation calculations and is continuously injected into the RO inlet. Regular membrane flushing is also useful: at each system stop, the membranes are flushed with low TDS water (product water or soft water) to prevent concentrated water from standing on the membrane, which reduces the risk of scaling. It is critical to keep the cross-flow velocity sufficiently high, especially in order to avoid deposits in the first elements; in the design, the production flux values are chosen conservatively according to the fouling tendency of the water (for example, low fluxes such as 10 L/m².h are used in wastewater recovery). In hot climates, pipelines and equipment are protected from the sun with insulation and, if necessary, cooling is provided to prevent biofouling. In summary, fouling prevention is a multifaceted approach: good pretreatment + appropriate chemical dosing + operational measures (regular flush, appropriate recovery rate, reasonable flux values) are applied together.
Membrane Cleaning (CIP) and Maintenance
Despite all precautions, RO membranes need periodic cleaning over time. Cleaning (CIP) is done with chemical solutions circulating in place, without removing the membranes from the system. The usual practice is to use different chemical recipes sequentially for different types of fouling. For example, first an acidic cleaner (low pH) is used to dissolve inorganic scales such as calcium carbonate, metal hydroxide; then an alkaline cleaner (high pH, detergent) is used to soften and remove organic and biological fouling. If biological film is present, enzymatic cleaners or non-oxidative biocide solutions can also be used. During cleaning, a chemical solution heated to 30–40°C is typically passed through the membranes at low flow and circulated for a while. The system is then rinsed and the next chemical is used. A CIP cycle can last several hours. The frequency of cleaning depends on water quality and operating conditions; Generally, CIP 3-6 times per year is acceptable, but in some difficult wastewater treatment plants, monthly cleaning may be required. Normalized permeate flux and pressure difference are monitored to determine the need for cleaning; cleaning is generally recommended when a 10-15% flux loss or a 15-20% delta-P increase is observed. If the membrane is cleaned correctly, the original performance is largely restored. However, over time, membranes age and losses accumulate that are not completely restored by cleaning; in this case, it may be necessary to replace the membrane elements after a certain number of years (typically 5-7 years). In addition to regular CIP, preventive maintenance is also carried out to extend the life of the membranes: For example, the membranes of an RO system that will not be used for a long time are kept wet with biocidal preservation solutions (otherwise drying out and biogrowth may be damaged). In addition, O-ring seals, fittings and instrument calibrations are checked and replaced periodically. General maintenance activities such as pump maintenance and filter element replacement should also be carried out without interruption.
Efficiency Increase Methods
Energy consumption and water yield are the two most important parameters in terms of efficiency in reverse osmosis systems. The use of energy recovery devices (ERD) is common, especially in large-scale facilities. In seawater RO plants, energy costs can be reduced by 30-60% thanks to pressure exchangers that recover the energy of the high-pressure concentrated stream and transfer it to the feed water. These devices have become standard in modern SWRO units. In addition, choosing high-efficiency types in pumps (e.g. variable-speed turbo pumps) and minimizing pressure losses in pipelines also increase energy efficiency. New generation membranes with high permeability provide energy savings because they can provide the same flux at lower pressure; for example, nanocomposite membranes or thin-film nanoporous membranes developed in recent years have higher water permeation coefficients. Sequence optimization and return ratio adjustment are another issue for efficiency: Instead of very high recovery in a single stage, an optimized recovery divided into two stages usually reduces the total energy cost and cleaning requirement. For example, instead of a single stage of 75%, a two-stage design of 50% + 50% reduces the risk of scaling as it provides a lower maximum concentration, thus consuming less chemicals. Automation and intelligent control also increase efficiency; advanced control systems prevent both energy and water waste by optimizing pump pressure and valve settings according to changing conditions (feed salinity, temperature, desired production flow). They also reduce system downtime by detecting and eliminating faults early. Membrane modifications (making the surface hydrophilic, anti-fouling coatings) are also applied in commercial products and indirectly increase efficiency by delaying fouling formation. Finally, there are R&D studies on reusing concentrated water; for example, recovering a little more water by performing a second advanced treatment of RO concentrate or crystallizing salts from concentrate and circulating water (ZLD – zero liquid discharge) are applied in some plants. Although such applications are currently high-cost, they may become widespread in the future, especially in regions with strict environmental restrictions, and maximize water efficiency. In summary, technological and process improvements are evaluated together to increase energy and water efficiency in the dynamic operation of reverse osmosis systems; thus, the sustainability of the RO process is constantly improving.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a method with its own pros and cons among water purification technologies. Comparing it with other technologies with similar purposes (e.g. distillation, ion exchange, nanofiltration, etc.), we can summarize its advantages and disadvantages as follows:
Advantages
High purification efficiency: RO is one of the methods that provide the highest removal rates for many contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, harmful chemicals, bacteria and viruses. A properly designed system can remove 95-99% of most ions. This allows a wide range of raw waters to produce reliable quality product water. For example, RO is able to produce drinking water from salty seawater or to make arsenic-containing groundwater safe; conventional methods cannot achieve this level of purification in a single step.
Wide range of applications and flexibility: Reverse osmosis systems can be scaled from small-scale home purifiers to large city water treatment plants. Since they are modular, it is relatively easy to increase or decrease capacity. In addition, membranes can be selected according to specific needs (low energy requirement, high rejection, fouling resistance, etc.) and adapted to the application. This flexibility has made RO the choice of different sectors.
Energy efficiency compared to other methods: Compared to technologies such as distillation, RO generally consumes less energy per unit of water. Especially in seawater desalination, modern RO systems do the same job with much lower energy consumption. While thermal methods require high heat energy because they are based on evaporation of water, RO uses only pressure energy and offers the possibility of energy recovery. This makes it preferred in large-scale applications.
Low chemical consumption: While alternatives such as ion exchange systems regularly use acid/alkaline chemicals for resin regeneration, there is no significant chemical consumption during RO operation (apart from pretreatment chemicals and cleaning). This provides advantages in both operating costs and environmental loads. Since product water quality is directly based on physical separation, no unwanted by-products are added to the water.
Simultaneous removal of many contaminants: Since the RO membrane acts as a barrier, inorganic salts, organic molecules and microorganisms in the water are removed together in a single step. For example, instead of a separate process for softening + nitrate removal for hardness removal, RO can handle them all at once. This integrated treatment feature simplifies the process line. It also significantly reduces contaminants that are difficult to remove with traditional methods, such as boron, arsenic and fluoride.
Disadvantages
High energy demand and pressure requirement: Since RO is a pressure-operated process, energy consumption can be significant, especially in high-salinity waters. For example, seawater RO, despite advanced recovery techniques, still consumes many times more energy than low-pressure applications such as bottled water treatment. This is a disadvantage in areas where energy costs are high or energy resources are limited. In addition, powerful high-pressure pumps and their electrical infrastructure are required for the system to operate, which increases investment costs.
The problem of concentrated effluent (brine): Perhaps the biggest environmental disadvantage of reverse osmosis is that it produces a concentrated effluent stream containing separated salts and contaminants. This concentrated water can be harmful to the environment if its disposal is not carefully managed. Even if this effluent is discharged into the sea at sea, the impact of salinity on the local ecosystem must be considered. In inland areas, the concentrated water is usually discharged into sewers or disposed of in evaporation ponds, both of which add additional costs and environmental burdens. Unless zero discharge (ZLD) systems are installed, RO always produces a effluent stream and cannot use 100% of the water.
Fouling and maintenance requirements: RO membranes require more delicate maintenance compared to other filtration systems. If the feed water is not properly conditioned or the system is not operated correctly, the membranes can quickly become dirty and clogged. This means frequent cleaning or membrane replacement. Problems such as biofouling and scaling on the membrane surfaces require interruption of operation and chemical cleaning; this leads to both water production interruption and chemical usage. For example, treating high iron or highly organic water with RO may require intensive maintenance. In this respect, RO requires more “gentle” operating conditions, requires qualified personnel and regular monitoring.
Membrane and equipment life: The typical life of membrane elements in reverse osmosis systems is around 5-7 years (depending on water quality and maintenance). After this period, membrane performance may deteriorate to an unacceptable level and replacement is necessary. Membrane replacements are an additional cost to the operating cost. In addition, equipment such as high-pressure pumps and pressure vessels may wear out; seals and o-rings should be replaced periodically. In other words, RO systems involve consumable and replacement costs in the long term.
Non-selectiveness and removal of beneficial minerals: Since RO retains almost everything in water without distinguishing between beneficial and harmful, it also removes beneficial minerals when it comes to drinking water. Beneficial ions for human health such as calcium and magnesium are almost zero in RO product water. For this reason, some users describe RO water as “dead water” and need to add minerals again. Similarly, RO water that is completely free of minerals may not be suitable for direct use in plant watering or aquarium applications, and may need to be balanced. Although this is not a technical disadvantage, it may require additional processing depending on the purpose of use.
High initial investment cost: Especially large capacity reverse osmosis plants can be expensive to install. When you consider quality membrane elements, stainless piping, high pressure pumps, energy recovery units, instrumentation and automation, the installation cost of an RO plant can be high compared to alternatives. Although it is generally more economical compared to alternatives such as distillation, it is definitely more costly than simple filtration or softening systems. Therefore, simpler solutions can be preferred instead of RO for small-scale and low TDS water needs.
While the advantages of RO make it a key technology in water treatment, its disadvantages require the correct selection of the application area and careful system design. In general, RO may be an unnecessary cost when very high purity is not required; however, when it is needed, there seems to be no other technology that can replace it. In recent years, improvements in membrane efficiency and energy recovery methods have reduced the disadvantages and increased the appeal of RO. Nevertheless, concentrate waste and fouling issues should be carefully managed in terms of the environmental sustainability of RO plants. For example, if there are wastewater discharge restrictions in a region, the project should not be implemented without special treatment or disposal plans for RO concentrate.
Conclusion and Evaluation
Reverse osmosis systems are advanced technologies that meet today’s water treatment and desalination needs with high efficiency and reliability. As discussed in this report, reverse osmosis reverses the natural osmosis phenomenon and separates water molecules from contaminants through semi-permeable membranes. This has made it possible to produce drinking water from salty seawater, recycle wastewater, and provide ultrapure water for industries. RO systems are a multi-stage process from pretreatment to high-pressure pumps, membrane modules to final conditioning. Each stage is critical to final water quality and system performance. A properly designed and operated RO plant produces consistent quality water despite fluctuations in feedwater conditions.
The success of reverse osmosis continues to increase, largely due to improvements in membrane technology and process optimization. The development of more durable, fouling-resistant and high-permeability membranes, reduced energy consumption and new generation control systems have made RO systems much more efficient and user-friendly than in the past. Energy recovery devices in particular have dramatically reduced the costs of seawater desalination, accelerating the shift to RO in water-scarce countries.
However, there are important issues to consider in RO applications. Environmentally friendly management of the concentrated waste stream, optimization of the water recovery rate, effective pretreatment for fouling control and implementation of maintenance programs are essential for the sustainability of the system. Despite its disadvantages, reverse osmosis offers a more economical, safe and comprehensive solution in most scenarios when compared to alternative methods. For example, distillation methods not only remove salt but also all non-volatile substances, but their energy consumption is very high; ion exchange is selective and targets only certain ions, constantly consuming chemicals. RO, on the other hand, can achieve the same results that these methods can provide together when integrated correctly.
When we consider the future, as access to clean water resources becomes more difficult due to the increasing world population and climate change, the strategic importance of reverse osmosis and similar membrane technologies will increase. RO will play a critical role in both creating new water resources through seawater desalination and providing a circular water economy through the recycling of urban wastewater. Research and development studies are focused on further improving membranes, reducing operating costs and finding innovative solutions for the disposal of concentrated waste. For example, topics such as recovering valuable minerals such as lithium and magnesium from concentrated streams or RO systems operating with solar energy have the potential to improve both the economic and environmental performance of RO.
In conclusion, when properly planned and operated, reverse osmosis systems are powerful tools that reliably improve water quality and secure water supply. In order to maximize the advantages and minimize the disadvantages of this technology, a holistic approach should be adopted: Feedwater analysis, appropriate pretreatment, membrane selection, energy optimization, waste management and regular maintenance should all be considered together. From an engineering perspective, reverse osmosis requires interdisciplinary system integration, and a successful RO plant represents a harmonious combination of fields such as materials science, chemistry, fluid mechanics and control engineering. In our increasingly water-scarce world, advanced treatment technologies such as reverse osmosis will play a key role in building a sustainable water future.